Table of Contents
1. The Core Technical Innovation: The Self-Contained Research Loop
Traditional brainstorming puts all the pressure on you.
You start with an idea, open a search engine, scan links, open multiple tabs, read bits and pieces, and then try to connect everything in your head. The process is slow, distracting, and mentally exhausting because you are doing the searching, filtering, and organizing at the same time.
But with Perplexity AI it creates a self-contained research loop. It keeps your entire thinking process in one connected flow rather than spreading it across dozens of tabs and documents.
How the research loop works
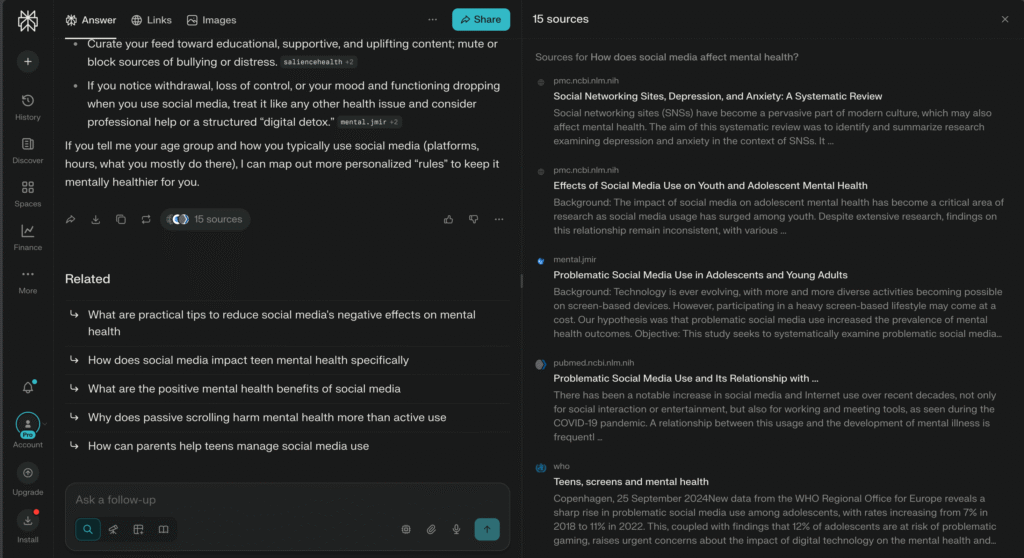
For example you asked question:
“How does social media affect mental health?”
As you can see in Pic 1, Perplexity then:
- Searches across multiple reliable and up-to-date sources
- Synthesizes the information into a short, easy-to-understand explanation
- Shows clear citations for every major point
At this stage, you already have something better than a normal search result: a verified starting point instead of raw links.
What makes it different from normal searching
The real difference appears after the first answer.
You don’t need to leave the page or restart your research. From the same response, you can:
- Click a citation to explore a specific study or article
- Ask a follow-up question based on something that caught your attention
- Use related questions to explore nearby ideas without losing context
Each new question builds directly on the previous one. Your thinking becomes continuous instead of fragmented.
Why this matters for brainstorming
Because everything happens in one place:
- Your ideas develop step by step, not randomly
- You always know where your information comes from
- Your brainstorming session becomes a clear, traceable process
Instead of holding everything in your head, you end up with a documented trail of thinking that you can later turn into an essay, outline, or research paper.
The key takeaway
Perplexity doesn’t just help you find information faster.
It changes how you think while researching.
By keeping searching, reading, questioning, and verifying inside one loop, it turns brainstorming into a focused, low-stress process and this loop is the foundation for every advanced technique explained in the next sections.
2. Citation-Chain Exploration: Turning Answers into Better Ideas
Most students treat citations as something you deal with after writing a boring requirement at the end.
That’s a mistake.
With Perplexity AI, citations are not the finish line. They are the starting point for deeper thinking.
This approach is what I call citation-chain exploration.
What usually happens with research
In a normal workflow, you search for a topic, skim an article, copy a few lines, and move on. If the article mentions another study or researcher, you usually ignore it because chasing references feels like extra work.
As a result, your ideas stay surface-level and your topic looks similar to everyone else’s.
How citation-chain exploration works
When you ask Perplexity a broad question, it gives you a clear answer with sources attached to specific claims. Each citation is a doorway, not a footnote.
Instead of just reading the summary, you look closely at where the information came from.
For example:
- One citation might reference a 2024 academic study
- Another might point to a recent policy report
- A third might mention a researcher or institution by name
Now comes the key move.
You don’t open random links. You ask a new, focused question based on one strong source:
- “Explain this 2024 study in simpler terms.”
- “What other work has this researcher published recently?”
- “What criticisms exist of this study’s conclusions?”
Each question follows directly from a citation in the previous answer. That’s the “chain.”
Why this creates better essay topics
This method does something powerful:
- It pushes you beyond generic overviews
- It leads you into specific debates, gaps, and disagreements
- It naturally produces narrower, more original angles
Instead of writing about a huge topic like “AI and education,” you end up with something much stronger, such as:
- a particular study
- a disputed finding
- or a recent shift in expert opinion
That’s exactly the kind of thinking professors reward.
Why this is better than Google
Search engines give you everything at once and leave you to decide what matters. Perplexity does the first filtering for you, then lets you drill deeper only into high-quality sources.
You’re not wandering. You’re following a guided path through credible research.
The key takeaway
Citation-chain exploration turns brainstorming into a targeted research process.
You stop collecting random information and start building ideas by following the strongest evidence step by step. By the time you start writing, you already understand the conversation around your topic not just the basics.
This is how brainstorming quietly turns into serious academic work.
3. Provocation-Driven Ideation: Finding Strong Ideas Through Disagreement
Most brainstorming focuses on finding support for an idea.
That’s useful, but it often leads to safe, one-sided topics/opinions that don’t stand out.
A more powerful approach is to look for tension.
This is where Perplexity AI becomes especially valuable not as an answer machine, but as a critical thinking tool.
The problem with one-sided brainstorming
When you only ask questions like:
- “What are the benefits of AI in education?”
- “How does social media help democracy?”
You usually get predictable answers. Your essay ends up explaining something everyone already agrees with, which limits originality and depth.
Strong academic writing lives in the space between competing ideas.
How provocation-driven ideation works
Instead of asking Perplexity to agree with you, you ask it to challenge you.
You deliberately prompt it to surface:
- Counter-arguments
- Contradictory evidence
- Recent studies that question popular claims
For example, instead of asking:
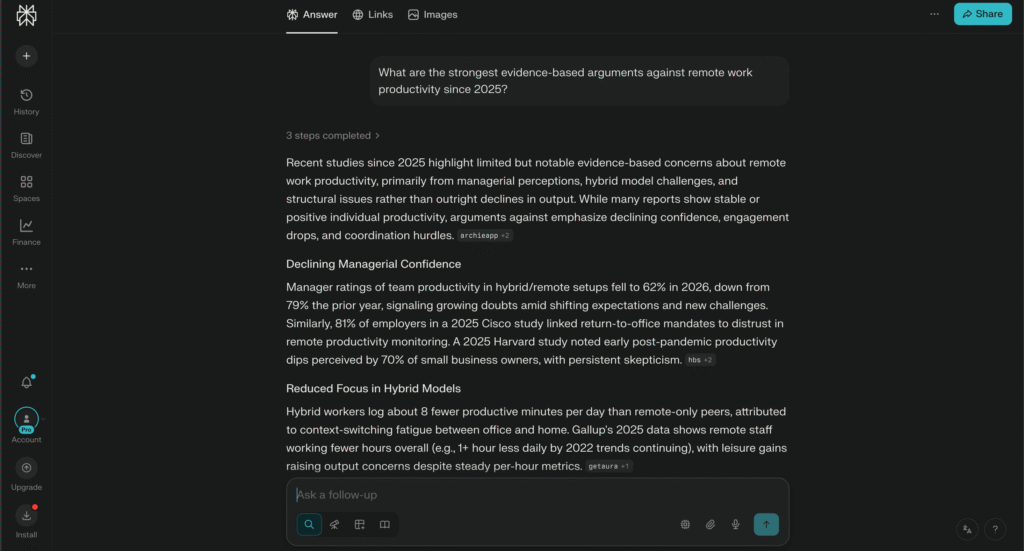
- “How does remote work improve productivity?”
You ask:
- “What are the strongest evidence-based arguments against remote work productivity since 2025?”
Perplexity then:
- Searches recent research
- Summarizes opposing viewpoints
- Cites credible sources for each challenge
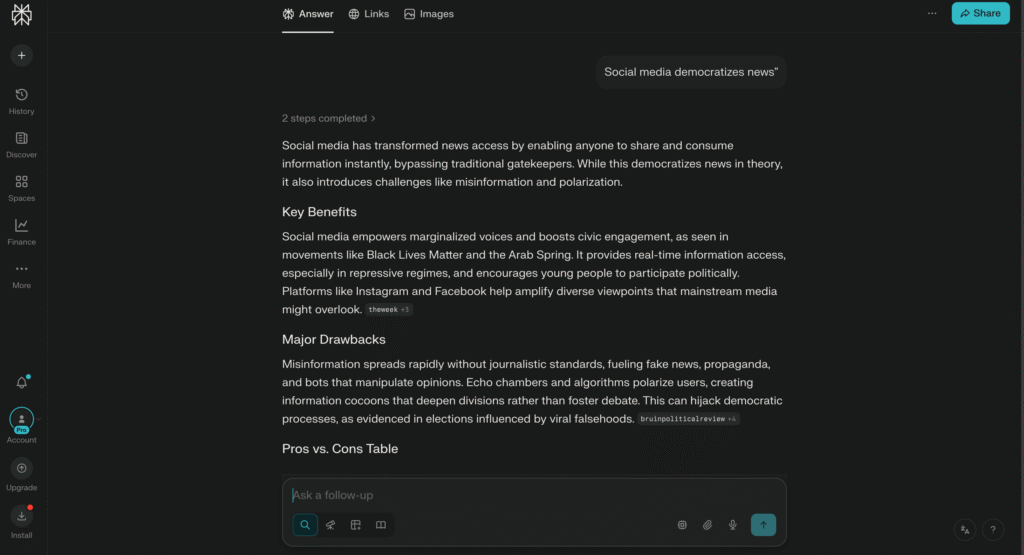
You are no longer brainstorming in a straight line. You are exploring conflict and you can clearly see the difference in answers between Pic 2 vs Pic 3.
Why this creates better essay topics
This approach naturally leads to stronger ideas because:
- You see where experts disagree
- You identify gaps, limits, and trade-offs
- You move beyond simple explanations
Instead of writing:
- “Social media democratizes news”
You might develop:
- “How algorithmic amplification undermines the democratic promise of social media”
That shift from agreement to tension instantly makes your topic more analytical and more interesting.
Why this is hard without AI
Finding strong counter-arguments manually takes time. You’d have to:
- Search for critical papers
- Filter opinion pieces from evidence
- Compare multiple viewpoints
Perplexity shortens this process by actively looking for opposition while still grounding everything in citations.
The key takeaway
Provocation-driven ideation helps you brainstorm ideas that are:
- More critical
- More balanced
- More academically valuable
By using AI to challenge your thinking instead of confirming it, you reach deeper, more original essay topics faster and with clearer evidence.
This technique is where brainstorming starts to feel like real scholarly thinking.
4. The Academic Focus Funnel: From Broad Ideas to Clear Essay Topics
One of the hardest parts of brainstorming is not finding ideas it’s narrowing them down.
Many students start with topics that are either:
- Too broad to handle properly
- Too vague to turn into a strong argument
This usually leads to frustration and last-minute topic changes.
This is where Perplexity AI helps by acting like a research funnel.
The common problem with topic selection
A typical starting idea might look like:
- “Climate change”
- “Artificial intelligence”
- “Mental health and social media”
These topics are not wrong, but they are unfinished. On their own, they’re too big to research deeply within an essay or paper.
The mistake most people make is trying to narrow these topics on their own, without enough context.
How the Academic Focus funnel works
Instead of jumping straight to a final topic, you move through the research in stages.
You begin broad:
- “Explain circular economy models.”
Perplexity gives you:
- A clear overview
- Key subtopics
- Credible sources
Then you narrow the focus:
- “What problems exist in applying circular economy models in fashion?”
Finally, you sharpen it:
- “What gaps exist in implementing circular economy practices in the U.S. fast-fashion industry since 2025?”
At each step, your question becomes more specific, more researchable, and more original.
Why this feels easier than traditional research
Because Perplexity summarizes and cites information at every stage:
- You always know why you’re narrowing the topic
- You don’t guess which angle is important
- You avoid choosing a topic that’s either too simple or too complex
Your topic evolves naturally instead of feeling forced.
Why professors value this kind of focus
Essays built this way:
- Show clear thinking
- Address a specific problem or gap
- Are easier to support with evidence
Rather than describing a whole field, you are engaging with a precise issue inside it.
The key takeaway
The Academic Focus funnel helps you move from:
- “I don’t know what to write about”
to - “I know exactly what question my essay is answering”
By narrowing your ideas step by step with evidence guiding each decision you turn a broad interest into a strong, manageable, and well-defined research topic.
5. Comparative Lateral Analysis: Creating Unique Ideas by Connecting Unrelated Fields
Important note: The goal of comparison here is not to force weak analogies or replace subject-specific research. Comparisons should be used only as a thinking aid to reveal patterns, ask better questions, and inspire original angles while still relying on credible sources within the primary field of study.
Most brainstorming stays inside one subject.
If the topic is economics, you only read economics.
If it’s biology, you stay inside biology.
That’s safe but it also produces predictable ideas.
This is where Perplexity AI enables a much more creative approach called comparative lateral analysis.
Why most ideas sound the same
When everyone researches the same field using the same sources, they end up with similar arguments and examples. Even if the writing is good, the thinking feels familiar.
Original ideas often come from connections, not depth alone.
How comparative lateral analysis works
Instead of staying inside one domain, you intentionally ask Perplexity to compare two different systems, even if they seem unrelated at first.
For example:
- Biology and economics
- Ecology and technology
- Psychology and social media design
You might ask:
- “Compare how ecosystems stay resilient with how decentralized financial systems handle failure.”
- “Compare attention in human psychology with engagement design in social media platforms.”
Perplexity then:
- Explains both systems clearly
- Highlights structural similarities and differences
- Cites sources from both fields
You’re no longer just learning facts. You’re seeing patterns.
Why this leads to standout essay topics
When you connect ideas across fields:
- Your topic becomes interdisciplinary
- Your argument feels fresh, not recycled
- You demonstrate higher-level thinking
Instead of writing:
- “How blockchain works”
You might write:
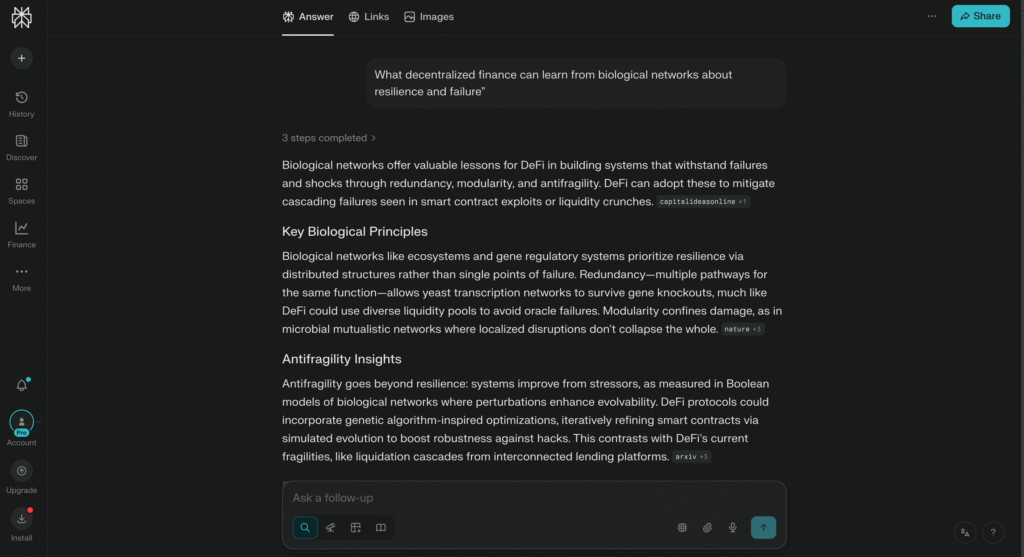
- “What decentralized finance can learn from biological networks about resilience and failure”
That kind of topic immediately signals originality as you can see in Pic 4.
Why this is hard to do alone
Making these connections manually requires:
- Knowledge of multiple fields
- Time to learn unfamiliar concepts
- Confidence that the comparison actually makes sense
Perplexity lowers this barrier by explaining both sides clearly and grounding the comparison in real sources.
The key takeaway
Comparative lateral analysis helps you move from:
- Learning within a subject
to - Thinking across subjects
I know it may sound ridiculous but this can be really, if you don’t want to do it and take any chances thats totally fine, on contrary i would recommend you to be safe when it comes to academics but you can try it for fun who knows maybe it can produce something extra ordinary.
6. Temporal Trend Mapping: Moving From “What Is” to “What’s Next”
Important note: Future-focused analysis is not prediction or speculation. It is a reasoned extension of recent, well-documented evidence. All forward-looking discussion should be grounded in credible sources and presented as possibilities, not certainties.
A lot of essays get stuck describing the present.
They explain what happened, summarize current debates, and stop there. That’s fine, but it’s also where many papers start to feel ordinary.
What really strengthens an idea is the ability to ask: Where is this going?
This is where Perplexity AI becomes useful for temporal trend mapping understanding how recent developments point toward future outcomes.
The common limitation in student research
Most research stops at:
- “This is how things work today”
- “This is what experts currently say”
But many fields technology, economics, policy, environment are changing fast. Writing only about the present can make your work feel outdated almost immediately.
How temporal trend mapping works
Instead of asking Perplexity only to explain a topic, you ask it to analyze recent evidence over time.
For example:
- “Summarize major changes in AI regulation since 2023.”
- “Based on 2024–2025 research, what challenges are likely to emerge next?”
Perplexity then:
- Pulls from recent reports and studies
- Identifies patterns and shifts
- Grounds future projections in cited evidence
You’re not guessing. You’re reasoning forward from what’s already documented.
Why this creates stronger arguments
This approach helps you:
- Show awareness of recent developments
- Demonstrate forward-thinking analysis
- Move from description to evaluation
Instead of writing:
- “Current AI laws focus on data privacy”
You can explore:
- “Why current AI regulations may fail to address enforcement challenges faced by startups in the next few years”
That shift instantly adds depth.
Why this matters academically
Professors value work that:
- Engages with recent sources
- Shows awareness of direction and impact
- Treats research as an evolving conversation
Temporal trend mapping shows you’re not just repeating information you’re thinking critically about its implications.
The key takeaway
Temporal trend mapping helps you move beyond static research.
By using recent evidence to project likely future issues, you turn your brainstorming into insight-driven analysis. This makes your ideas more relevant, more thoughtful, and better suited to subjects that are actively changing.
7. Spaces as an External Brain: Turning Research Into a System
By the time you’ve brainstormed for a while, the real problem isn’t ideas.
It’s keeping everything organized.
Notes are in one place.
Links are in another.
Good ideas are scattered across tabs, documents, and random screenshots.
This fragmentation is what makes research feel messy and overwhelming.
This is where Perplexity AI introduces one of its most practical features: Spaces.
The usual problem with organizing research
Traditionally, you might:
- Save links in a browser
- Take notes in a document
- Keep ideas in your head
None of these are truly connected. When it’s time to write, you have to mentally reconstruct everything often under deadline pressure.
How Spaces change the workflow
A Space works like a dedicated research workspace.
Inside a Space:
- Every question you ask is saved
- Every answer keeps its citations attached
- You can add your own notes, links, and comments
Instead of loose pieces, you get a single, connected research environment.
What makes this powerful for brainstorming
The real advantage appears once you’ve collected several questions and sources.
You can then ask Perplexity a new question based on everything already inside that Space. It synthesizes:
- Your saved research
- Your previous questions
- Live, up-to-date sources
Your brainstorming session becomes something the AI can help you analyze, not just store.
Why this feels like an “external brain”
Because:
- You don’t have to remember everything
- You don’t lose good ideas
- Your thinking stays visible and structured
Instead of holding the entire project in your head, you offload it into a system that keeps working with you.
Why this matters when it’s time to write
When deadlines approach:
- You already have organized sources
- Your key ideas are clearly mapped
- Your research has a logical flow
Writing stops feeling like starting from scratch and starts feeling like assembling something you’ve already built.
The key takeaway
Spaces turn brainstorming from a chaotic activity into a repeatable process.
By externalizing your thinking and letting AI synthesize across your own saved research, you move from scattered ideas to clear structure without extra tools or stress.
This is where all the previous techniques come together and become usable in real academic work.
Conclusion
Brainstorming doesn’t have to feel chaotic or overwhelming. With the right approach, it can become a structured process where each question builds on the last and every idea is supported by real sources.
Perplexity AI stands out because it keeps research, thinking, and organization in one place. By using techniques like citation-driven exploration, focused narrowing, and organized Spaces, you spend less time searching and more time understanding.
Used responsibly, these methods can help you develop clearer ideas, stronger arguments, and a more confident research workflow. The goal isn’t to replace your thinking it’s to support it, so you can approach assignments with less stress and better direction.
Disclaimer: I am not a professional researcher, academic advisor, or educator. The ideas and techniques shared in this article are based on personal analysis, experimentation, and general research practices and are intended for educational and informational purposes only. These methods are designed to support brainstorming, research exploration, and critical thinking—not to replace original analysis, academic judgment, instructor guidance, or institutional policies. Readers should verify sources and use AI tools responsibly as research assistants, not as substitutes for their own work.